Now that you know how to call yourself using the Voice API, learn how to handle incoming calls.
Before you can get started, you need the following already set up:
- Set all Voice API configuration settings.
- Python and a familiarity with how to create a new file.
- PIP (package installer for Python) and a familiarity with how to install Python modules.
- Flask and a familiarity with how to set up a Flask environment and app.
- ngrok. You'll use ngrok to open a tunnel to your local server.
Now you can start setting up your environment.
Create a new folder where you want your app project and open a command prompt to that location. Create a new environment with the following command:
py -3 -m venv venvActivate the environment using the following command:
venv/Scripts/activate
The easiest way to install the SDK is using pip:
- Open a command prompt or terminal to the local repository folder.
- Execute the following command:
pip install sinch
We will be using Flask to create a lightweight webserver that will listen for requests from the Sinch servers to handle incoming calls. Additionally, we'll be using the requests module to parse incoming HTTP requests.
Use the following commands to install the Flask and requests modules:
pip install Flask, requests- Create a new file named
app.pyand paste the provided "app.py" code into the file.
# Use this code to responde to an incoming phone call using the Voice API and Python SDK.
from sinch.domains.voice.models.svaml.actions import HangupAction
from sinch.domains.voice.models.svaml.instructions import SayInstruction
from flask import Flask, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/', methods=['POST'])
def result():
incoming_call = request.get_json()
print(incoming_call)
if (incoming_call['event'] == 'ice'):
svaml_response = {
"instructions": [
SayInstruction(text="Thank you for calling. This call will now end.").as_dict()
],
"action": HangupAction().as_dict()
}
return svaml_response, 200
else:
return "OK", 200- Save the file.
Now you can start your server with the following command:
flask runAt this point you need to start your ngrok tunnel so that the Sinch servers can access the webserver running on your local machine. Run the following command to start your tunnel:
ngrok http [YOUR_SERVER_PORT]Replace [YOUR_SERVER_PORT] with whatever port on which your server is listening. This starts a tunnel to your webserver.
Copy the http ngrok URL. Navigate to your app on your dashboard. Under the Settings section, you'll see a field labeled "Callback URL." Paste your ngrok URL into that field and click Save.
Now your server is listening and your callback URL is configured, so you're almost ready to test everything and make a phone call. But before we do, let's take a closer look at callbacks. If you already know about callbacks, skip right to calling your Sinch phone number.
Callbacks (also known as "webhooks") are the method that the Voice API uses to figure out what you want to do with a call. Basically, a callback is a request that the Sinch servers send to your server whenever something happens (otherwise known as an "event") in the call that requires some input from you. There are a few different types of events, but the two we are concerned about for this guide are the Incoming Call Event and the Disconnected Call Event.
An Incoming Call Event (or ICE) happens whenever someone calls one of your Sinch numbers. In essence, someone dials your number and so Sinch servers reach out to you and say "how do you want me to handle this call?"
Most callback events expect a response, depending on the event. The Incoming Call Event expects to receive back a SVAML object in response. You can read more about SVAML here, but just know that SVAML is a markup language Sinch developed to control calls.
The below diagram demonstrates exactly what's happening:
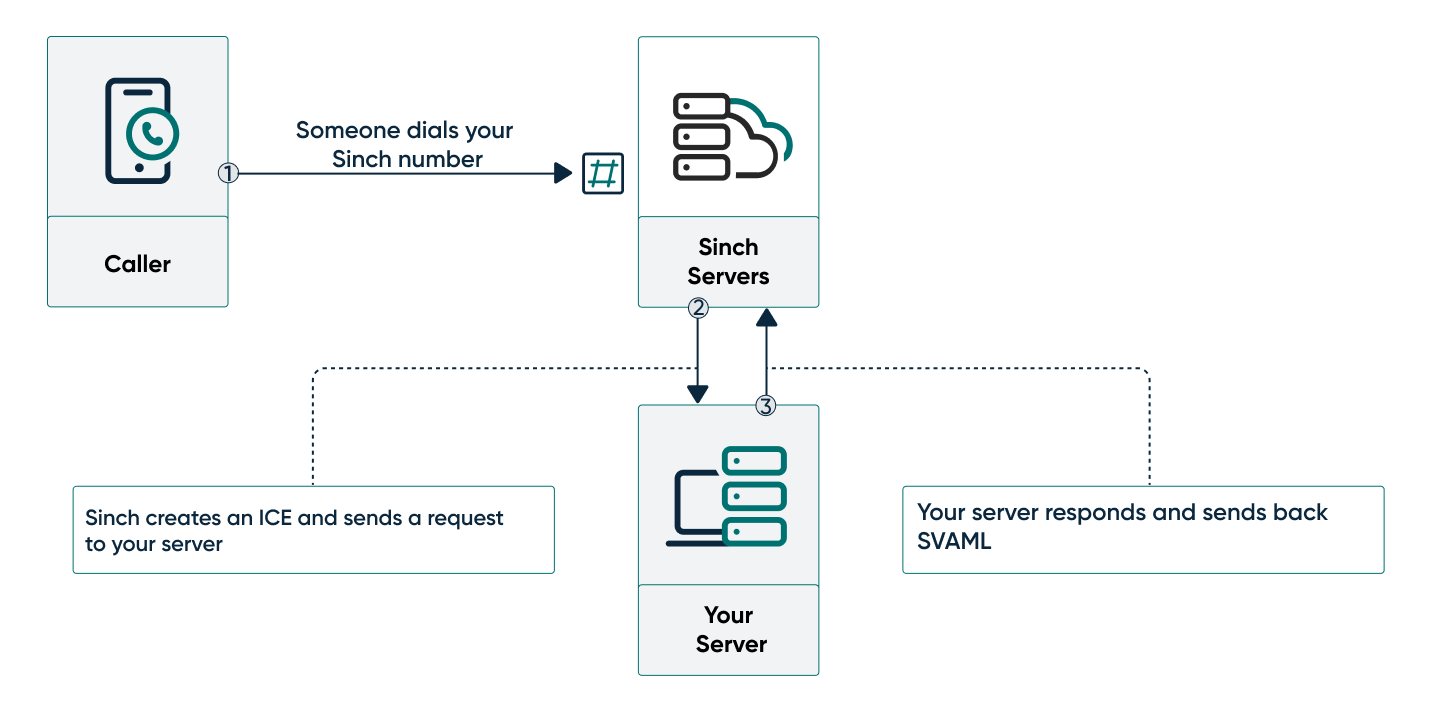
- Someone dials your Sinch number from a handset.
- The Sinch servers create an ICE and send a POST request to your server.
- Your server listens for the request and sends back a SVAML response to tell the Sinch server how to handle the call.
In this sample application, this is the SVAML object that you will use to respond to the callback (we've also provided the underlying JSON SVAML object for comparison):
svaml_response = {
"instructions": [
SayInstruction(text="Hi, thank you for calling your Sinch number. Congratulations! You just responded to a phone call.").as_dict()
],
"action": HangupAction().as_dict()
}This code creates a response that plays a Say instruction to read out a string of text and then hangs up the call to end it.
And that's it! Now we can test.
Look up the free Sinch number assigned to your app and call it using your phone. The call should be picked up by the Sinch servers and you should hear the text from the instruction. Now you know how to handle an incoming call.
Learn more about the Voice API: